Budget Templates for Everyone
What is a budget?
Financial planning for a set period of time is commonly known as budgeting. A budget is an estimate of revenues and expenses that a business is likely to bear in a given time period.
Budgets include incoming revenue forecasts (revenues and volume), operating expenses and any capital investments that an individual, family, or a business might be planning.
Budgets can be for short periods such as a week or month as well as longer periods such as for a year or more. The most common period for budgeting is one year, although it actually depends on the budgeting person’s personal preference and the relevant situation.
Once expected revenues and expenditures are drafted, a budget may be in surplus or deficit. A budget surplus is when expected incomes are higher than expenditures. In such a case, it is feasible to make plans on how to utilize leftover resources.
A budget deficit occurs when expected income is less than expenditures. In such a case, additional financial resource planning is required to finance the deficit. There are several ways to clear the deficit including cutting down expenditures, utilize savings or secure a loan.
How to make a good budget?
To make a sound budget the most critical factor is accuracy in predicting income as well as expenses. To make a good budget you must be able to predict income and expenses with certainty. Usually, if income through property, investments or wages and salaries are fixed, forecasting is not a problem. However, if income is expected to be variable than a good strategy is to use a historical average or alternatively moving average to forecast income.
The same goes for forecasting expenses as well. The next important step in making a good budget is to minimize expenses and prioritize them.
For example, if in a certain time period you have to choose between repairing a leaky roof or investing in air conditioning; you must be able to choose to get the roof repaired.
Prioritizing expenses can free up financial resources for later use and also provide leverage against unexpected circumstances. Finally, a good budget has very little difference than the actual budget if given circumstances are stable and supportive.
Benefits of Budgeting
Budgeting is essential whether you are managing personal expenses, managing a small business or a multinational. Budgets are useful for everyone. The benefits of budgeting are:
Mapping: Budgets map out what to expect in the near future. When the expected income is estimated, one can plan how much money would be available. This is helpful in planning and prioritizing expenditures.
Strategizing: Budgets are a key to devising future strategies/ plan of action for the given time period. Once you know how much income is expected, expenses can be prioritized on the basis of the budget. Thus budgeting enables one to plan out when and where to spend.
Efficient management: Budgets allow efficient management of limited financial resources as expenditures and income are forecasted. Thus important decisions can be made timely resulting in optimal resource utilization. Budgeting through efficient management can also aid in avoiding unnecessary financial losses. It can also help in repayment of the outstanding loan and prevent building up of debt.
Focus: Budgets allow one to remain focused on attaining both financial and non-financial goals. They constantly act as a reminder of what was initially planned. When you have a budget to follow, you have a goal and sense of purpose; therefore you abstain from making unnecessary
A budget as a tool for financial management
Budgets are the most important tool in financial management. They not only provide a benchmark for actual income and expenses but also provide control over the situation. Budgets help explain which income or expenses were unforeseen.
Benchmarking: Budgets act as a benchmark for actual expenses so that expenses can be tracked diligently and differences can be critically examined. This allows one to monitor income and expenses.
Control: Budgeting gives you control over your resources so you decide when, where and how to allocate resources. Budgeting allows you to be in charge of the situation and to reanalyze the plan-of-action if required.
Managing surplus and deficit: Budgets allow further planning regarding excess funds that could be better invested elsewhere. Alternatively, budgets enable financial managers to assess the situation and decide whether additional funding is required or not.
Different types of budgets
There are many different types of budgets including personal budgets, family budgets, educational budgets, government budget, business budgets and others.
Personal budget: A personal budget is usually kept by individuals who like to keep track of their income and expenses, who are saving up for something or have a certain goal to achieve. Personal budgets can be based on predictions about the monthly expenses and revenues or even longer term.
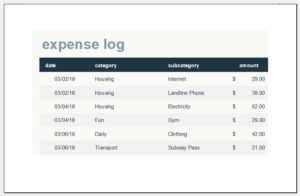
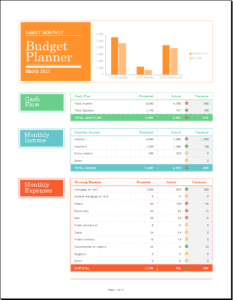
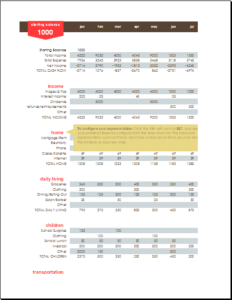
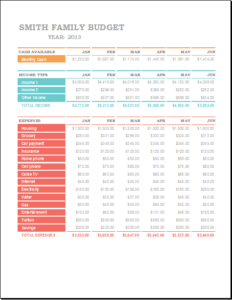
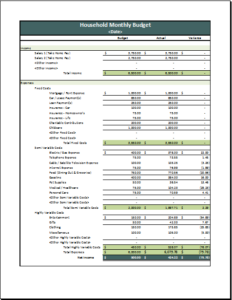
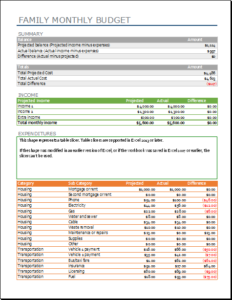
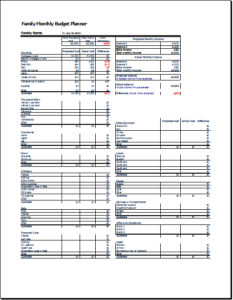
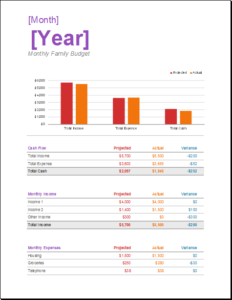
Family budgets: Some families are very good at maintaining and following budgets. Particularly, families with limited resources are most keen on making budgets to help them keep track of their goals and comfortably sail through the month or until the next income source is found. Family budgets include bills to pay, school fees for children, monthly groceries, entertainment, and savings for house, car, or travel.
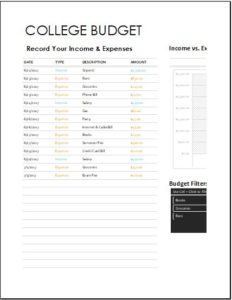
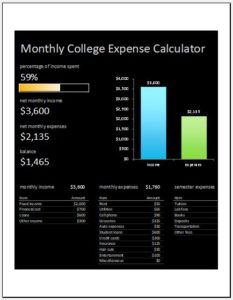
College Budgets: Students often find budgeting useful since they have limited resources. College budgeting includes identifying the source of income such as family support, scholarship or monthly stipend. College expenditures include expenditure on hostel accommodation or rental apartment, semester fees, books and stationery, clothing, food, and travel.
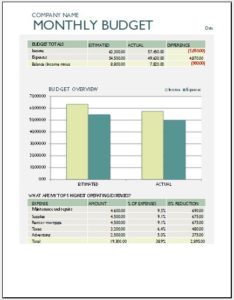
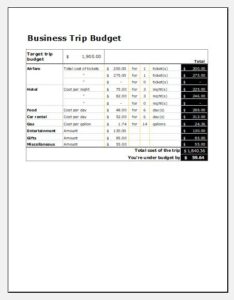
Business budgets: Businesses use budgets actively to manage their finances. Business budgets include income from the sale of goods and services. In addition, expenses range from utility bills, petty cash expenditure, procuring raw materials, salaries and wages, bonuses, rent of property and equipment, taxes and other items that fall under operating expenses.
← Previous Article
Office Supply Inventory List TemplateNext Article →
Small Business Inventory Spreadsheet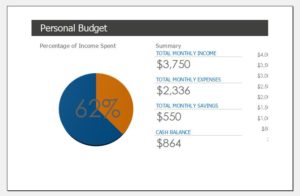



Leave a Reply